Table of Contents
Introduction
Website owners and digital marketers often face the nightmare of losing critical pages or entire sections of their website. Whether it’s due to accidental deletion, a failed migration, or a buggy plugin, missing content can impact traffic, user experience, and SEO rankings.
Two widely known tools for viewing lost content are the Wayback Machine and Google Cache. Both allow you to see snapshots of your website, but each has unique features, limitations, and use cases. In this article, we will explore both tools, compare their benefits, and provide practical guidance for website recovery. By the end, you’ll also learn how the Wayback Machine Downloader can help you efficiently restore lost content from either source.
1. What is the Wayback Machine?
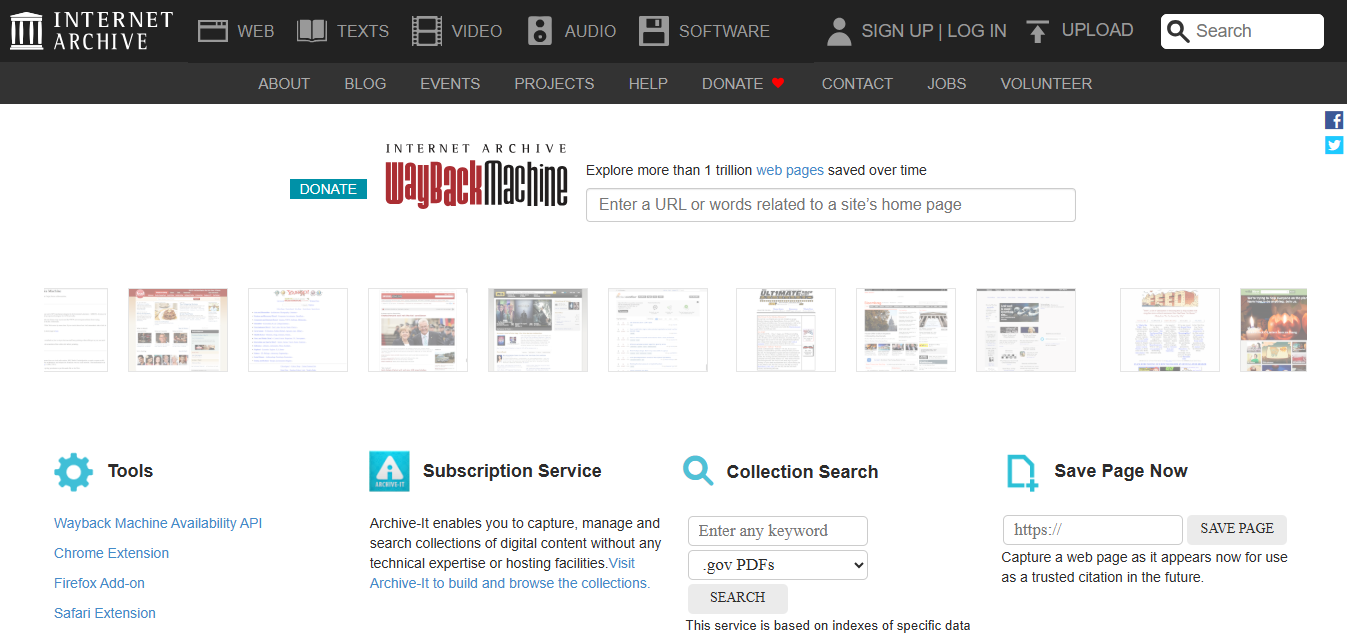
The Wayback Machine, created by the Internet Archive, is a digital archive that stores historical snapshots of websites. Since 1996, it has crawled and stored billions of pages, allowing users to view how a website looked at any point in time.
Key Features:
-
Provides multiple historical snapshots across years.
-
Stores HTML, images, CSS, and other website assets.
-
Useful for website audits, digital research, and recovering deleted content.
The Wayback Machine is a powerful tool for researching past content but is primarily designed for viewing, not downloading. Recovering an entire website manually from the Wayback Machine can be slow and cumbersome. For downloading and restoring website data, the Wayback Machine Downloader is the best tool, as it efficiently retrieves content from the Wayback Machine
2. What is Google Cache?
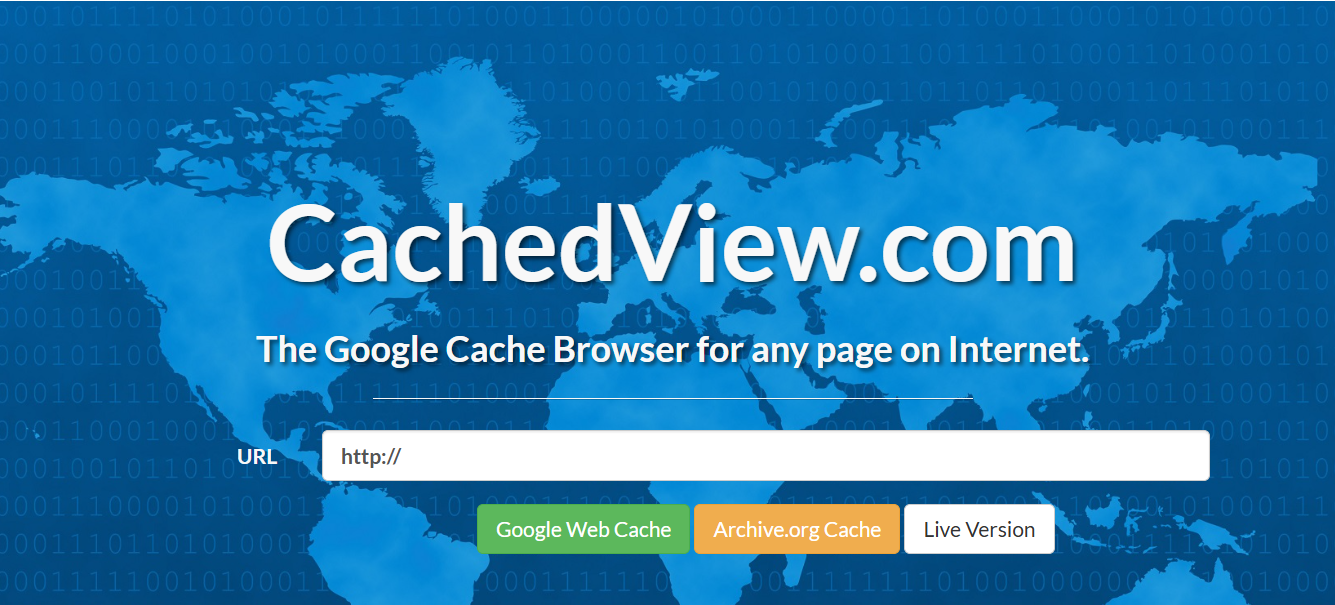
Google Cache is a temporary snapshot of a webpage stored by Google when its crawler indexes the page. It allows users to view a recent version of a page even if the live site is down.
Key Features:
-
Shows the most recent indexed version of a page.
-
Useful for checking content availability or quickly accessing a temporarily unavailable page.
-
Accessible via Google search results by clicking the “Cached” link next to the URL.
Google Cache is short-term and often replaced with the next crawl. It’s suitable for viewing recently deleted content, but not for recovering full websites or historical snapshots. For downloading and restoring website data, the Wayback Machine Downloader is the best tool, as it efficiently retrieves content from the Google Cache.
3. How Both Tools Work
Wayback Machine
-
Enter the URL of the website or page.
-
Browse the timeline to select the year of interest.
-
Click on a snapshot date to view the archived version.
-
Manually copy or save content if needed.
Limitation: You cannot easily download multiple pages or assets at once.
Google Cache
-
Search for the page in Google.
-
Click the three-dot menu next to the URL and select “Cached.”
-
View the most recent stored version.
-
Copy text or save images manually.
Limitation: Only one recent version is available, and it disappears once Google reindexes the page.
4. Benefits and Limitations of Wayback Machine
Benefits:
-
Access to multiple historical snapshots.
-
Stores complete page structure, including HTML, CSS, JS, and images.
-
Useful for recovering content deleted months or years ago.
Limitations:
-
Manual recovery can be time-consuming.
-
Not designed for large-scale downloads.
5. Benefits and Limitations of Google Cache
Benefits:
-
Quick access to recently deleted content.
-
Easy to view pages when a site is temporarily down.
Limitations:
-
Only the latest snapshot is available.
-
Cannot recover entire websites or multiple pages simultaneously.
-
Dependent on Google indexing; pages may not be cached if blocked.
6. Deep Comparison: Wayback Machine vs Google Cache
| Feature | Wayback Machine | Google Cache |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Coverage | Extensive (years/decades) | Limited (last crawl) |
| Content Access | Full HTML, CSS, JS, images | Mainly text and page rendering |
| Use Cases | Full website recovery, research | Quick content access |
| Ease of Download | Manual, time-consuming | Manual copy only |
| Reliability | High for older content | Low for old/deleted content |
Insight: While both tools allow viewing lost pages, the Wayback Machine is better for long-term recovery. Google Cache is temporary and best for recent mistakes.
7. Real-World Use Cases
-
Recovering an old blog post deleted months ago: Wayback Machine is ideal.
-
Checking how Google currently indexes a page: Google Cache works well.
-
Recovering multiple pages after a website migration: Wayback Machine is more efficient.
8. Best Practices for Website Recovery
-
Always maintain regular backups of your website.
-
Prioritize pages with high SEO value.
-
Use proper 301 redirects when restoring old URLs.
-
Update restored content with current information and optimize for SEO.
9. Introducing the Wayback Machine Downloader
While both the Wayback Machine and Google Cache have their uses, recovering content manually can be slow and limited. This is where the Wayback Machine Downloader comes in.
Key Features:
-
Can extract data from both Wayback Machine and Google Cache.
-
Allows you to download up to 10,000 files for free.
-
Handles HTML, CSS, JS, images, PDFs, and other website assets.
-
Ideal for full-site restoration, including historical snapshots.
-
For larger projects or complete domain recovery, users can contact our team for support.
This tool saves time, reduces manual work, and ensures reliable restoration of lost content. It’s the ultimate solution for marketers, website owners, and developers.
10. Conclusion
Both Wayback Machine and Google Cache serve important purposes for website recovery. Wayback Machine excels at historical content retrieval, while Google Cache is useful for quick access to recent changes.
However, for efficient, large-scale, and reliable recovery, the Wayback Machine Downloader is unmatched. It extracts content from both platforms, restores website assets, and provides an easy-to-use solution for all website restoration needs.
If you want to recover full website data, the Wayback Machine Downloader is your go-to tool. You can start by downloading up to 10,000 files for free. For larger restoration, contact expert team.
11. FAQs
Q1. Can I recover a deleted page using Google Cache?
Yes, but only if it was deleted very recently. Google Cache stores temporary snapshots, so the recovery window is limited.
Q2. Does the Wayback Machine store complete website files?
Yes, it archives HTML, images, CSS, JS, and sometimes PDFs. However, manual recovery can be time-consuming.
Q3. How does Wayback Machine Downloader help?
It allows you to download content from both Wayback Machine and Google Cache, including multiple pages and assets, saving time and effort.
Q4. Is there a free option for the Wayback Machine Downloader?
Yes, users can download up to 10,000 files for free. For larger restorations, you can contact the team.
Q5. Can I restore an entire domain?
Yes, with the Wayback Machine Downloader, large-scale restoration is possible with expert support.
Q6. Which tool is better for SEO purposes?
Wayback Machine Downloader is superior because it restores authoritative pages, links, and assets efficiently.
Q7. How do I select specific content from a date range?
With the Wayback Machine Downloader, you can choose a from-to date range to extract the data for specific snapshots.
Q8. Can I use the tool for competitor analysis?
Yes, you can study historical versions of competitor websites for insights.
Q9. Is my data secure when using the tool?
Yes, all data recovery operations are safe and private.
Q10. How fast is the recovery process?
It depends on the number of pages and files, but the tool is optimized for quick extraction and download.
Tag Post :



Responses